Information gathering is to collect as much information about our target, such as Domain Name Server (DNS) hostnames, IP address, and etc.
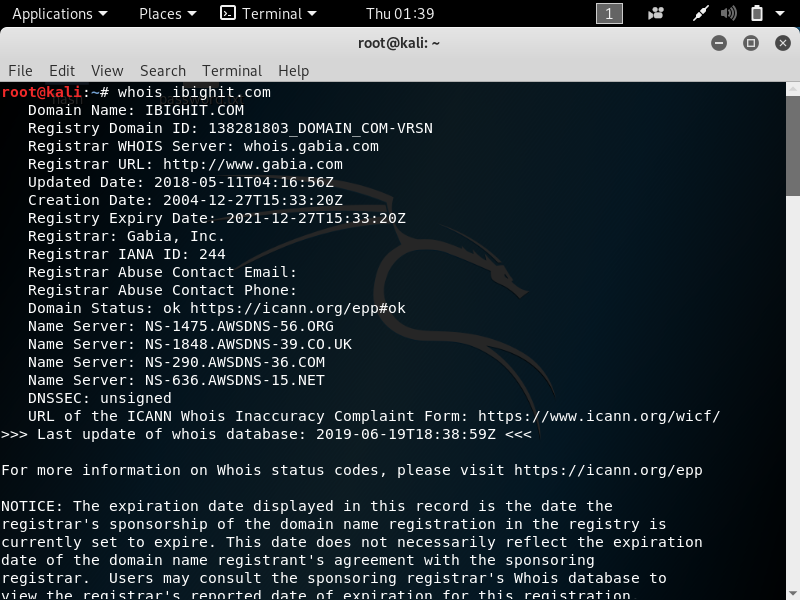
1. whois –> To gather information about the domain and the registrant.
The command is very simple –> whois *website*
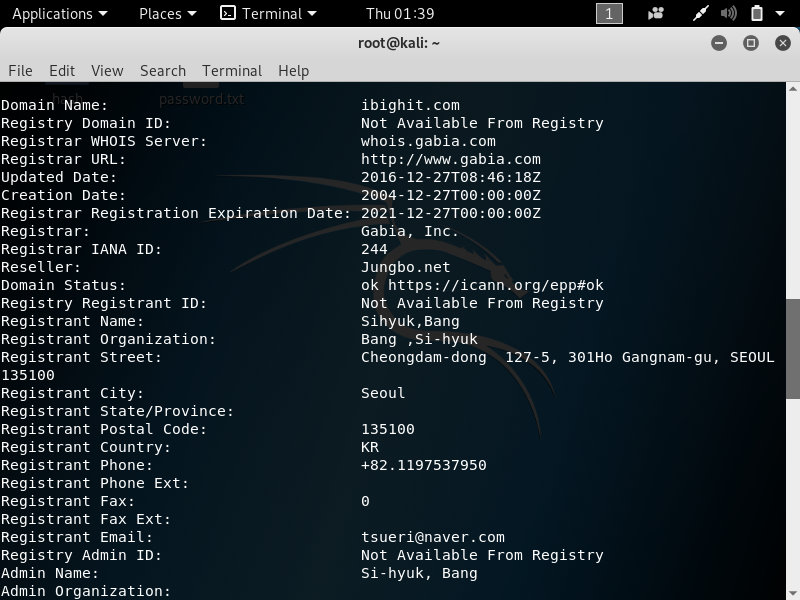
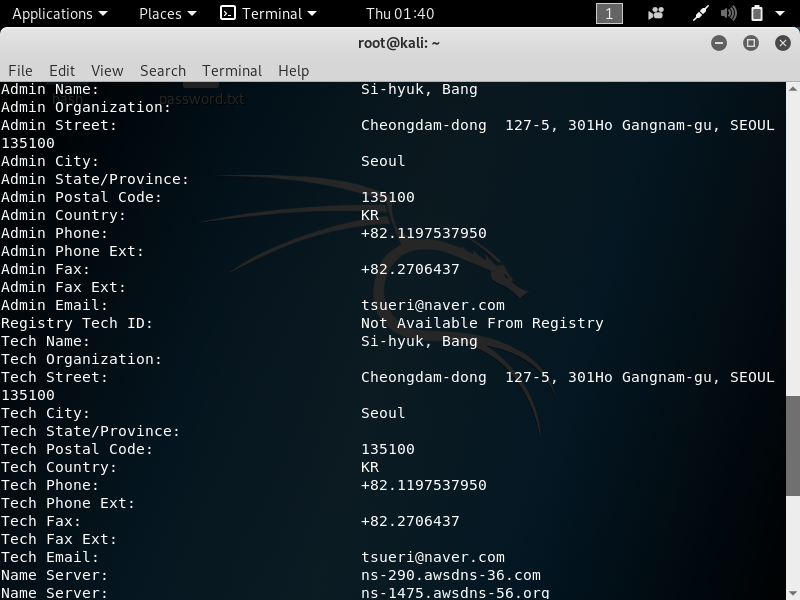
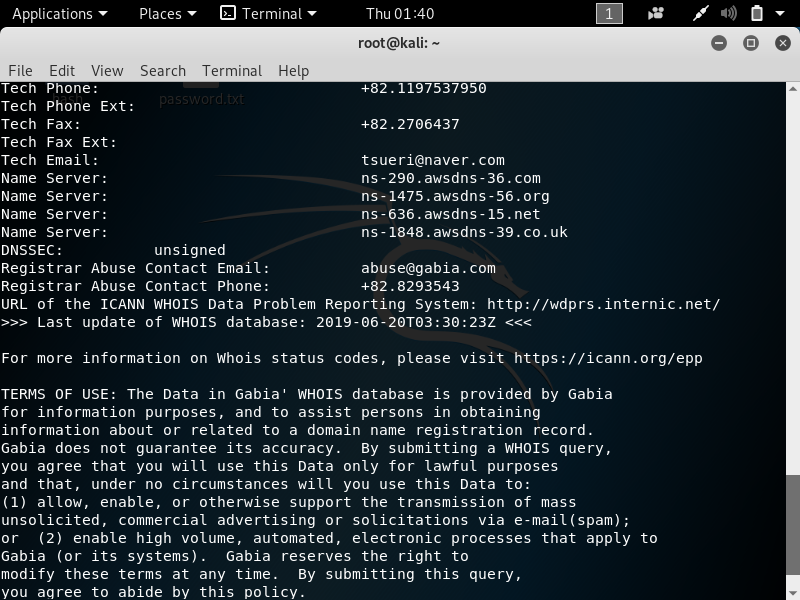
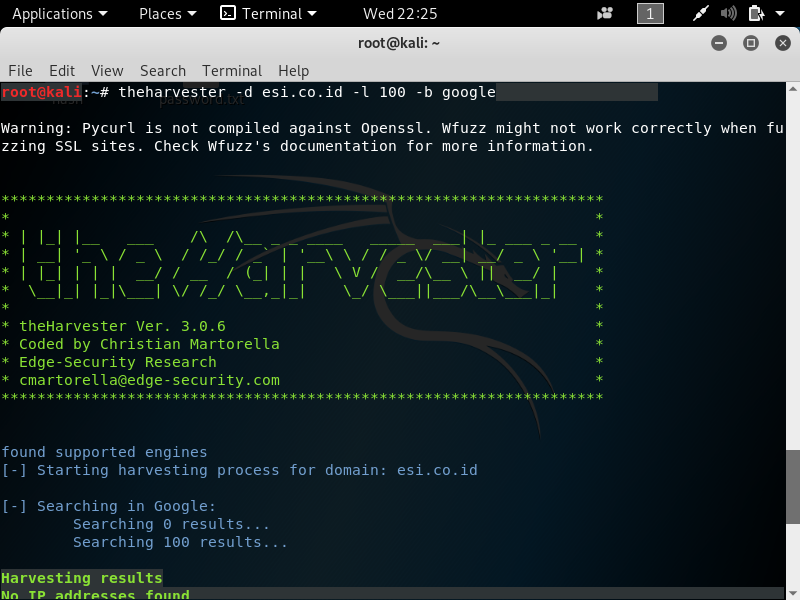
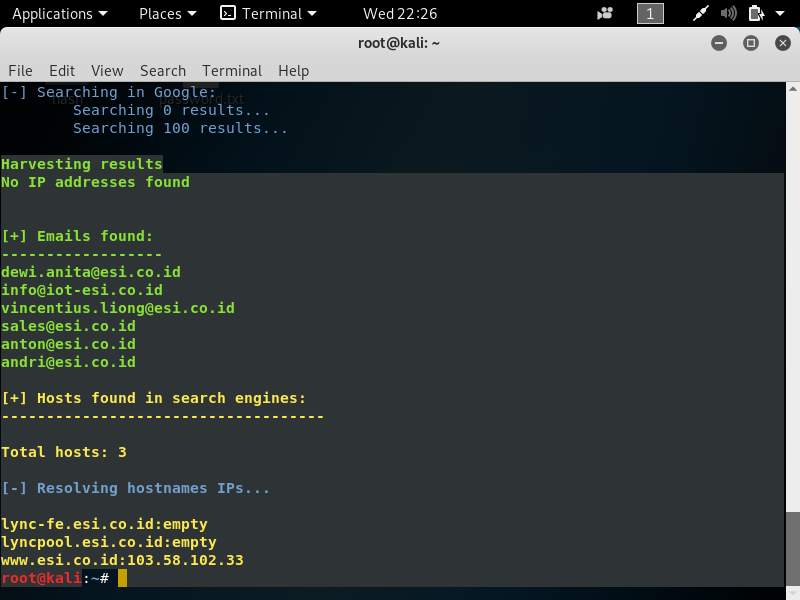
2. theHarvester –> To gather email account, username, and hostname.
If we want gather information using theHarvester, with maximum 100 results and using google the command is theharvester -d domain.com -l 100 -b google
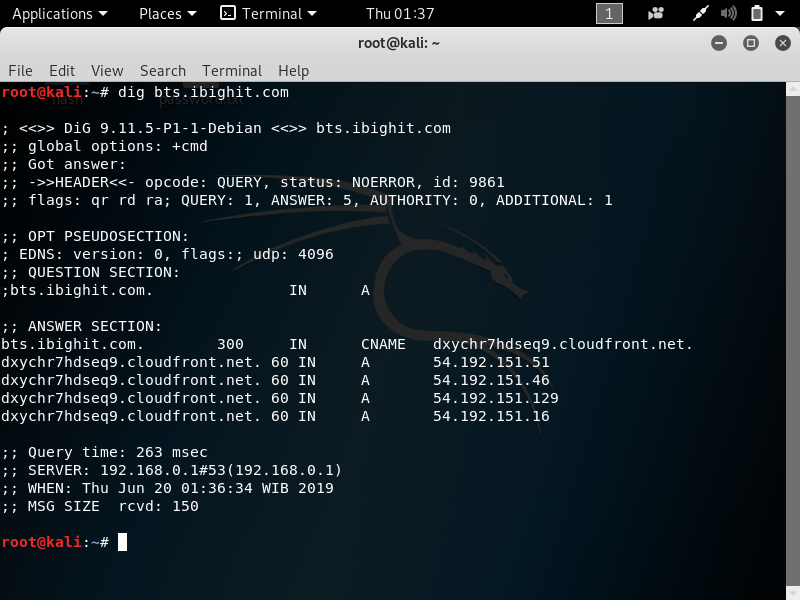
3. dig -> Dig (Domain Information Groper) is a network administration command-line tool for querying DNS name servers. It is useful for verifying and troubleshooting DNS problems and also to perform DNS lookups and displays the answers that are returned from the name server that was queried. The command is dig *website*


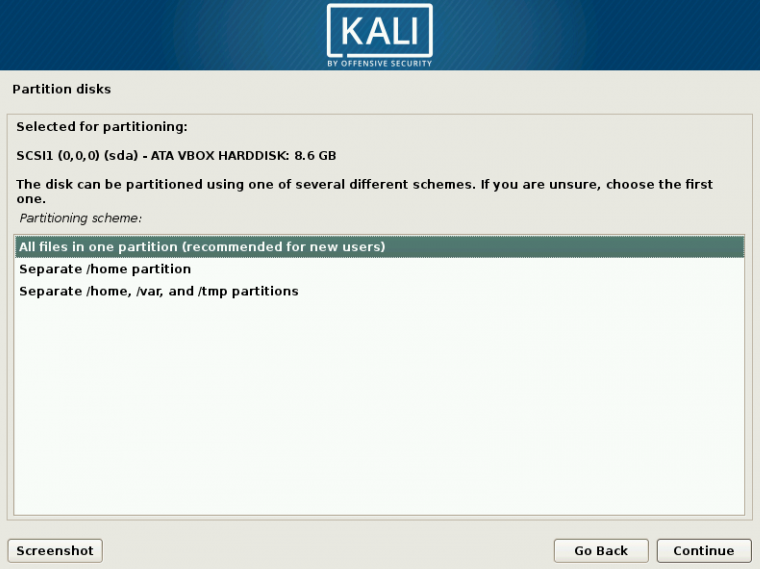
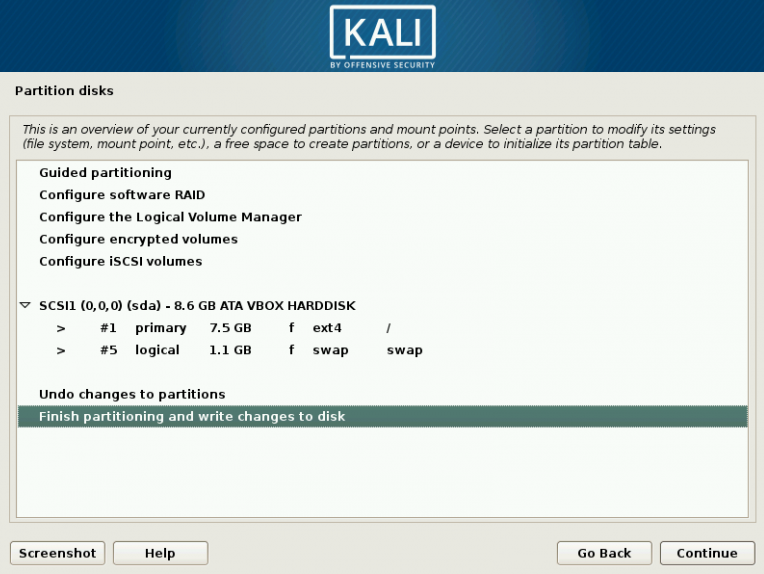
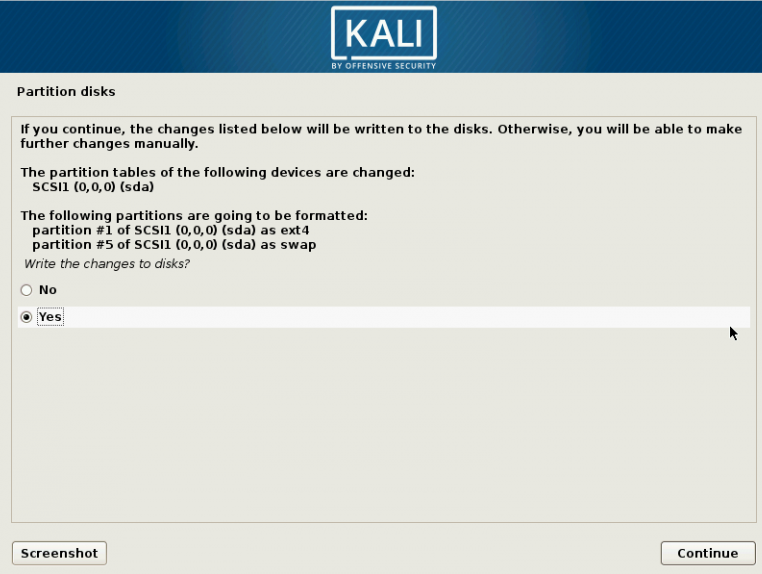
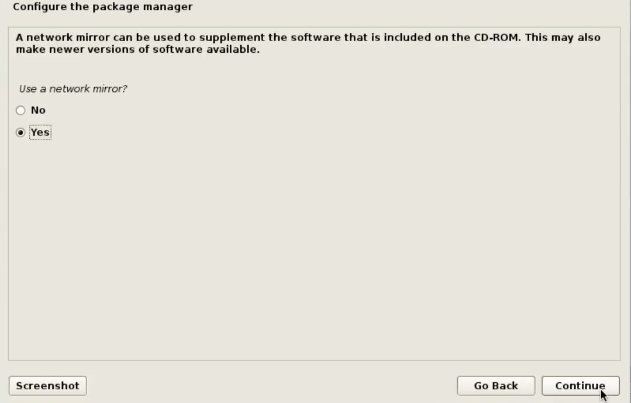
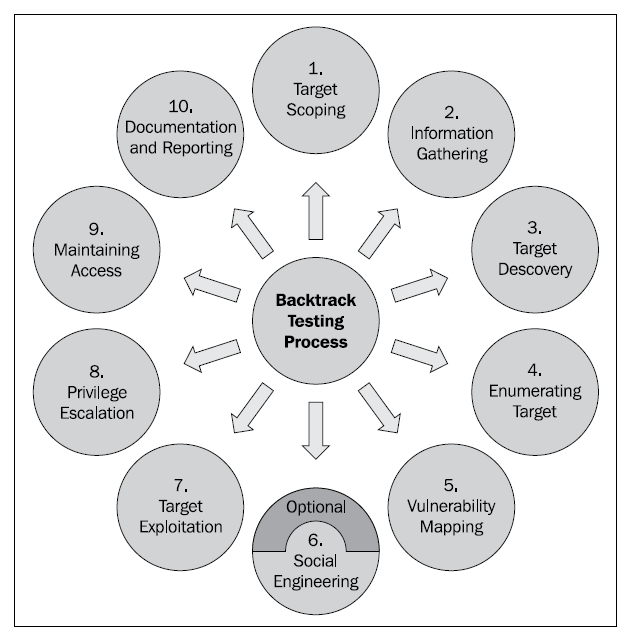 1 Target scoping
1 Target scoping